Mesopotamia: The land between two rivers
Introduction:
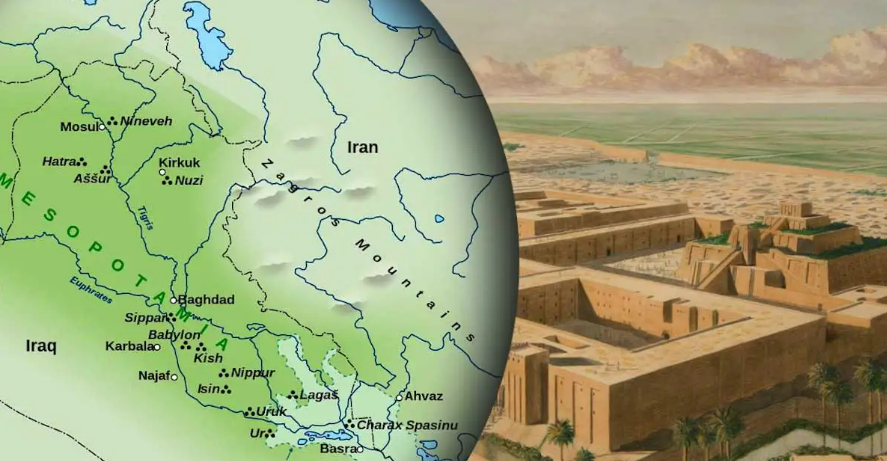
Mesopotamia is derived from a Greek word: ‘Mesos‘ ( in the middle of ) and ‘Potamos‘ ( rivers ). This means that Mesopotamia is the land between two rivers named Euphrates and Tigris. This is now the part of Iraq. In mesopotamia, cities were first developed and flourished. This land is mainly known for it’s prosperity, literature, astronomy, city life, mathematics and architecture.
Excavations began in 1840 and continued for decades. The Sumerian was the earliest known language in Mesopotamia, which later gave way to Akkadian. Mesopotamia was the place where writing was first developed. People used to draw thousands of signs on clay tablets to keep records. There were different types of cities developed in Mesopotamia: some cities and towns were developed around temples and other cities were based on trade.
Geography of Mesopotamia:

In North, there were steppes. One can consider steppes as small hills covered with grass. Specially after winter, goats and sheeps were fed on the grasses and low shrubs grown there. People preferred animal herding over agriculture. Mostly, shepherds used to take their herds for grazing.
In Northeast area, there were green undulating plains. There were enough rainfall to grow crops and channels of Euphrates and Tigris rivers were also the source of irrigation.
The desert covered the southern area. But mostly these desert areas supported the cities. Those things which supported cities the most are as follows:
- Silt deposited by river channels
- Flood in these channels ( for irrigation )
- People used to make small canals attached to their farms
The enough rainfall and silt deposited land made this land more productive. Not only through agriculture but also through sheeps and goats, they used to get their food. Some edible things available to them were:
- Fish
- Date-palm
- Milk
- Meat
What was the connection of Europeans with Mesopotamia?
Europeans had a strong connection with Mesopotamia as there they got a clay tablet depicting the similar story written in the old testament of Bible “The Book Of Genesis”. The story written in Bible was like: There was a man Nuah, appointed by God, to make a large boat. Actually, flood was about to come which could destroy everything. Nuah got a task to save some species from that disaster and god was going to save that boat. Nuah loaded pairs of each species and that’s how he completed his task. They drew a similar story on the clay tablet found in Mesopotamia, but the name of the man was different.
Many Europeans initiated excavations due to this similarity, and they continued them for decades. But in later years, Europeans considered the story of the Bible to be incorrect, so they returned to Europe and resolved all misunderstandings.
Importance of Urbanism:
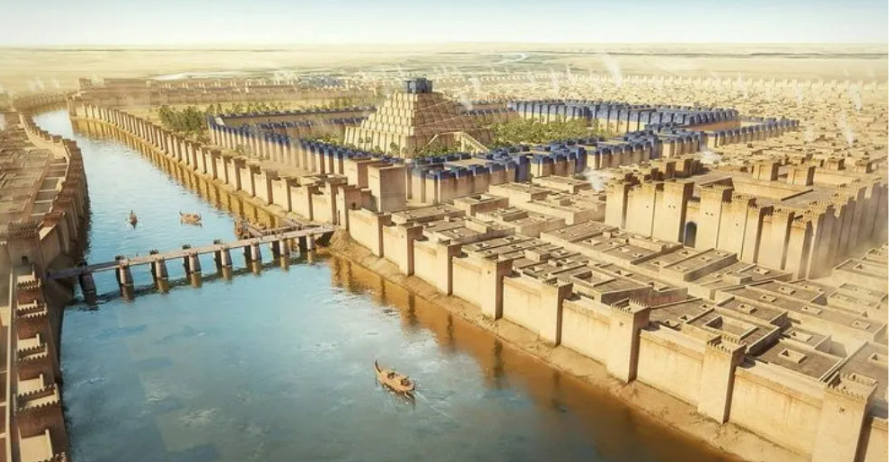

Cities are not only the places with large population. Urban economy comprises besides food production, manufacture, trade and services. Division of labour is the foundation of city life. Everyone became interdependent with the rise of cities and towns. In the development of cities, organised trade and storage is needed. Villages supply grains and other food items which are further processed or manufactured in the cities. Hence, to store and distribute those items wisely, there is a need to coordinate different activities and to keep written records.
Movement of goods:
There was a lack of mineral resources in Mesopotamia, southern part lacked stones, seals and jewels. Wood obtained from poplar tree was not that much good to make carts, cart wheels and boats. No metals were available there. So, they used to import those things in exchange of available things in Mesopotamia. Now, for this, efficient transport was needed. Modern logistics solutions, similar to the efficient trade routes used in ancient Mesopotamia, can be found today through services like Shiply, which offers hot shot trucking options for fast and reliable transportation.
Mainly, they used to travel through channels of Euphrates and Tigris rivers by boat. Because if they travel through carts, they will need to feed animals on the way which could be the wastage of time, energy and food. They used to trade for stones like lapis lazuli ( blue shiny stone ), vessels, seals, jewels, metals, etc. Warka Head was the sculpture found in Uruk, Mesopotamia. It was made by lapis lazuli for eyes, black stones for eyebrows and white marble for corneas of eyes. It was considered the best sculpture of that time. The attractive features of that was her chin, cheeks and eyes.
What was the need of writing?

Writing was used for these things:
- Keeping records
- Making dictionaries
- Narrating the deeds of the kings
- Giving legal validity
- Changes announced by kings in laws
By 2400BCE, Sumerian was replaced by Akkadian language. Cuniform signs represented were the syllables, not a single consonent or vowel. Writing was a skilled craft, it was also a intellectual achievement. Writing was seen as the sign of superiority in urban life.
Clay Tablets:
First writing was also emerged in southern part of Mesopotamia. There were scribes who were the professionals in writing as they had to learn thousands of signs. There was a story of king Enmerker who started the writing. He sent his messenger to another kingdom ‘Aratta’ for collecting precious stones but because of the months of travelling, he just forgot about it and came back without anything. King Enmerker made some signs or designs on the slightly wet clay tablet in cuniform shapes related to those things which he wanted. Upon seeing that, the king of Aratta was surprised and regarded King Enmerker as the most educated person.
The first clay tablet was written around 3200BCE. There was list of about 5,000 things like ocean, bread, ox, etc. These tablets were made to keep records. Once the record had ceased to be relevant, tablet had thrown away. To maintain new record, they had to make a new tablet for it. Scribes used to wet the clay first and pat it into the size that they could hold comfortably in one hand. They start to make signs on clay when it is little bit wet.
Why don’t they start writing after the clay dries?
Because once the clay get dry, it can break into pieces if we try to write anything on it specially with sharp ended reed cut plant.
Omen Tablets:
The people living there believed in so many superstitions. Such as:
- Raised threshold is the sign to be wealthy in the future. But threshold rose up because of the dirt swept out of their houses.
- If the front door of your house don’t open in front of other house that means you are lucky.
- If the wooden door of the opens outwards that means the woman will have more powers as compared to man in future.
Temples and Kings:
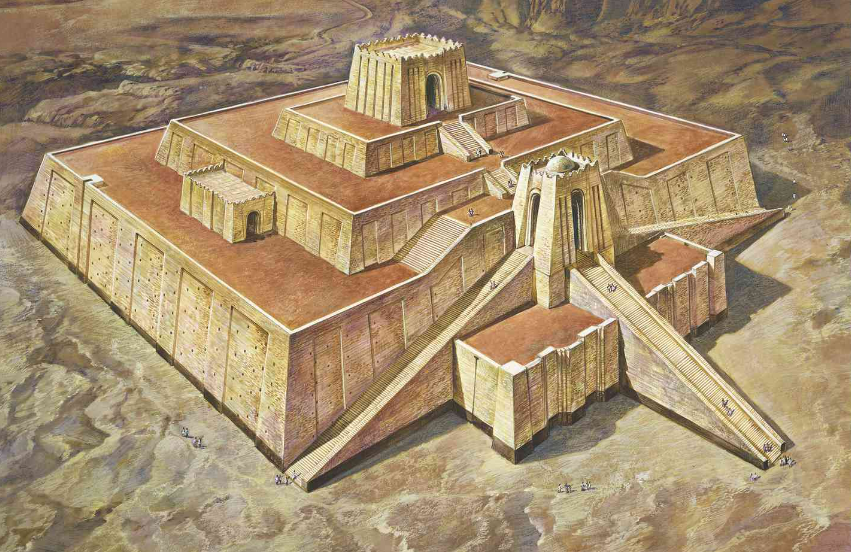

From 5000BCE, people started to settle in the southern part of Mesopotamia. Some cities started to develop around temples. People constructed the earliest temples using unbaked bricks. Gods they worshipped were:
- Ur ( the moon god )
- Inanna ( goddess of love and war )
Temples became larger over time. Outer walls were going in and out at regular intervals, there were several rooms and open courtyards in temples. People used to offer curd, fish and grains to gods. People considered gods as the theoretical owners of agricultural fields, fisheries, herds, and everything.
With time, the people in temples also began to process oil pressing, grain grinding, spinning, weaving, etc. Temples became the main urban institution. Activities like distribution and allotments of grains, breads, fish, etc. developed in the temples. There is a record that around 15,000 people worked 10 hours per day to built one of the temple in Mesopotamia and it took five years to complete it. But the main thing was that people were doing it happily with their willingness; they were not being forced to do it. The building up of that much big temple was very difficult. But those people could do anything on the name of god.
What were the problems faced by people in Mesopotamia?
There were both natural and man made problems. Natural problems were:
- If it doesn’t rain any year, it can lead to crop failure.
- Sometimes, too much water in river channels flood the crop.
- Sometimes, river changes it’s course
Man made problems were:
- Those who lived upstream could divert much water into their fields.
- Sometimes, they neglect to clean out the silt which used to block the further flow of water into downstream.
- There were repeated conflicts over land and water.
Because of these problems, wars were common in that region. And, the chief who emerged victorious used to distribute the loot between his followers. The victorious group made prisoners and slaves of the defeated people. Victorian chiefs used to offer precious booty in temples. They contributed in the beautification of temples too.
Town planning:
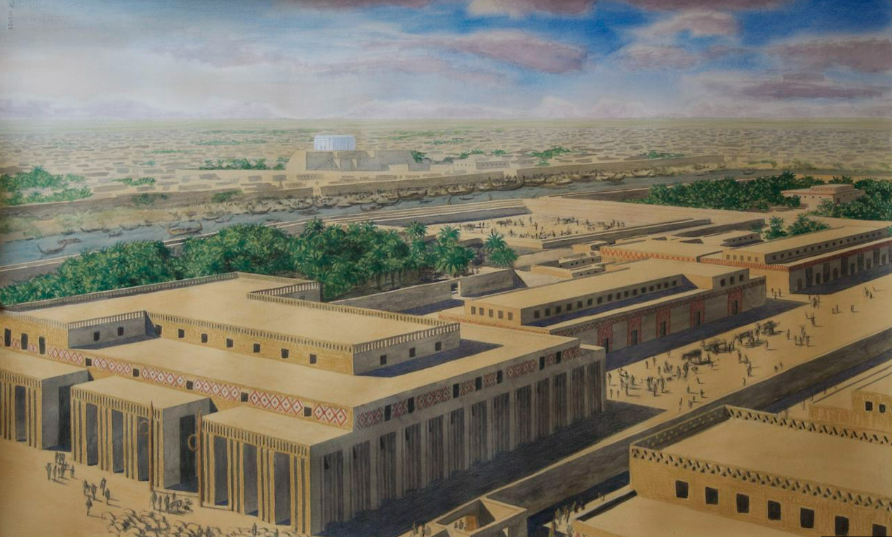

In 1950, archaeologists discovered narrow streets in Ur, a town in Mesopotamia. Because there wasn’t enough space for carts to enter the streets, people carried sacks of grains and other items on donkeys’ backs. There were the absence of street drains and proper town planning.
Researchers found drains and clay pipes in the inner courtyards of the houses. The residents sloped the house roofs inwards to collect rainwater into the courtyard, thus preventing the streets from becoming slushy.
People used covered basins in the ground, known as sumps, to store rainwater and drain water. People used to follow so many steps to prevent streets becoming dirty and slushy but they used to swept all the dirt of their houses in the streets because of which streets were rising up. That’s why, there was a need to rise the threshold of the houses time to time.
FAQ’s
Q1: What was the significance of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers to the Mesopotamian civilization?
The Tigris and Euphrates rivers provided fertile land for agriculture, facilitating the growth of settlements and the development of civilization. They also served as transportation routes for trade and communication.
Q2: How did Mesopotamian writing systems evolve, and what were their main forms?
Mesopotamian writing systems evolved from pictograms to cuneiform script, which consisted of wedge-shaped characters impressed onto clay tablets. The main forms of Mesopotamian writing included Sumerian, Akkadian, and later, Assyrian and Babylonian scripts.
Q3: What were the major contributions of Mesopotamian civilization to mathematics and astronomy?
Mesopotamian civilization made significant contributions to mathematics, including the development of a positional number system based on the number 60, which influenced later systems of measurement and timekeeping.
Researchers found some evidence proving that they were adept at solving questions related to squares, square roots, and tables. In astronomy, Mesopotamians were among the first to study celestial phenomena and develop rudimentary methods of predicting astronomical events, such as eclipses and planetary movements.
Q4: How did the fall of the Assyrian Empire contribute to the rise of other civilizations in the region?
The fall of the Assyrian Empire in the 7th century BCE created a power vacuum in the region, leading to the rise of other civilizations such as the Babylonian, Median, and Persian empires. These new powers inherited aspects of Assyrian culture and technology, contributing to the further development of Mesopotamian civilization.




